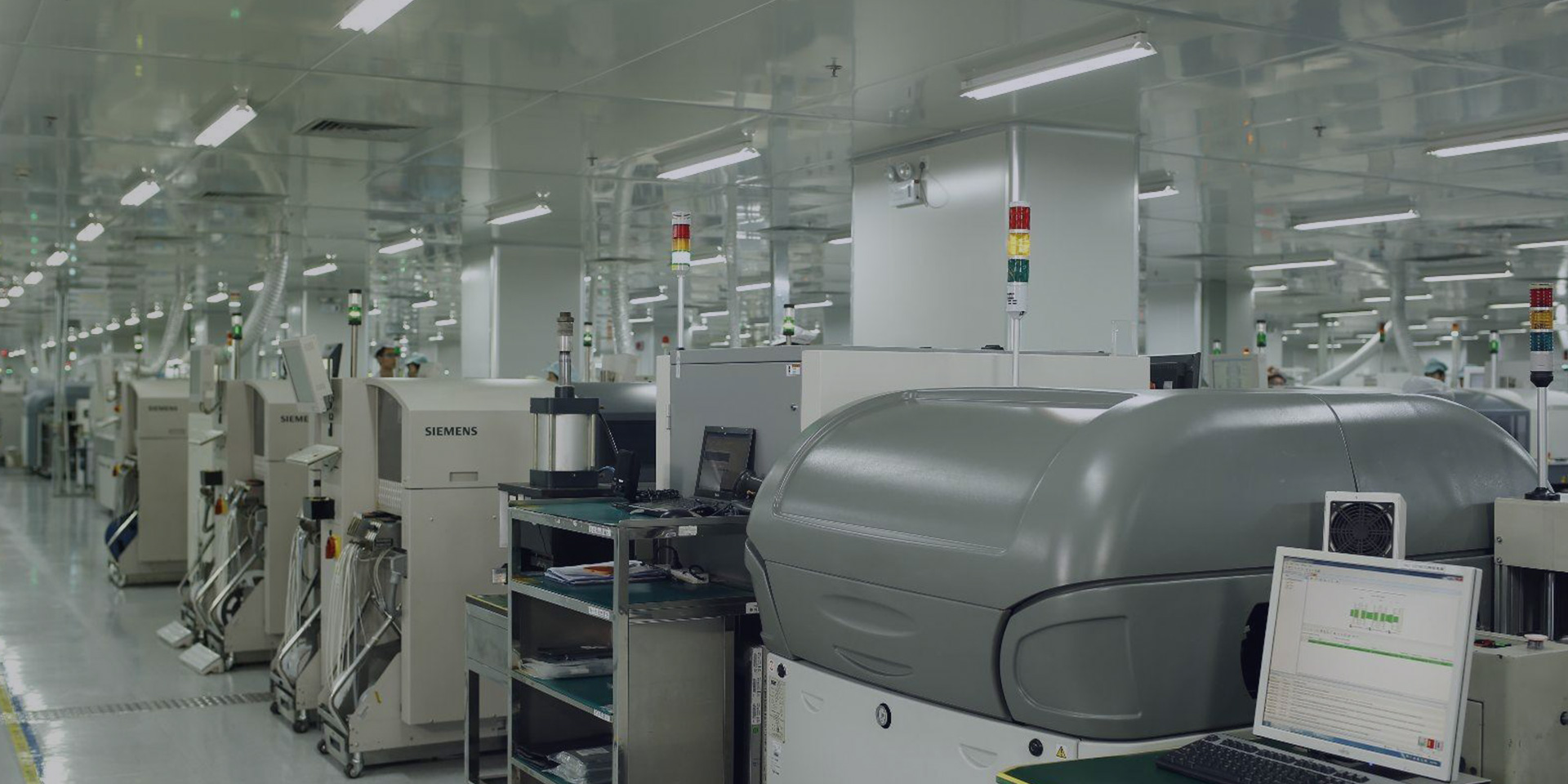

Electronic Manufacturing Service
Global PCBA small and medium batch express service provider, We provide one-stop service, allowing electronic engineers to realize ideas faster and better
99.5%
Client retention
100% satisfy clients in our work
18+
Years of experience
Fully on Electronic Manufacturing
1000+
Clients
1000+ customers 6000+ Engineers
10K+
Projects
99% successfully all project done
Electronic Manufacturing PROJECTS
Together We Will Drive Your Success



Our Services
Full Electronic Manufacturing Services

SMT ASSEMBLY
BGA\QFN package SMT processing

IC Programming
Online/Offline programming services

PCB MANUFACTURING
Rogers HDI Complext Board
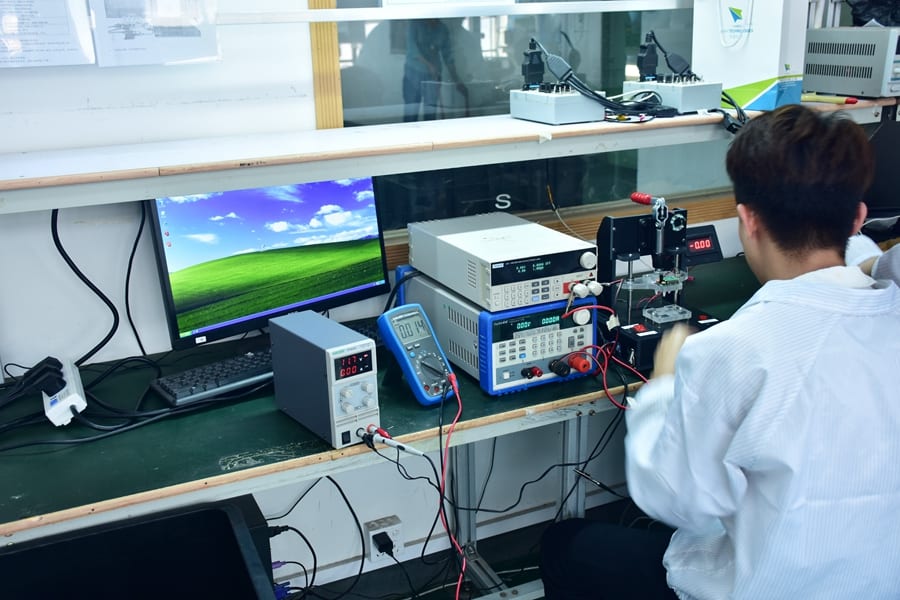

PCBA Testing
Provide test solutions according to functional requirements

COMPONENTS SOURCING
Full/Partial Parts source

Box Building
Full Box Building Assembly
Six Guarantees
Fully automatic SMT production line, 9 testing procedures, the ultimate experience of quality

Raw material guarantee
Imported solder paste brand Alpha Innovative LCR incoming material inspection system keeps out refurbished components and selects high-quality raw materials

Fast Delivery Guarantee
12-hour expedited service, normal delivery within 3 days, 4-hour delivery, the first time to ensure the interests of customers

Product Quality Assurance
High-precision SMT equipment and perfect DIP production line, the introduction of ESD electrostatic system supplied, X-RAY inspection BGM quality is reliable and stable
R & D Support
Own R&D team,Using technological innovation to improve production efficiency and quality,Have rich process experience to prevent quality risks

Strength guarantee
Mature management team, enterprising spirit of innovation, self-developed MES system, first article test system, dedicated service to every customer

Customer Service
Professional technology and rich process experience
Provide a complete PCBA solution
Strive to bring customers the most perfect cooperation experience

Who We Are
Electronic Contract Manufacturer
We provide professional electronic products processing, chip processing, plug-in processing, OEM, ODM foundry services, located in the PCBA R & D and SMT, DIP, assembly of high-end electronic manufacturing service providers, mainly serving domestic and foreign high-end PCBA rapid prototyping, industrial industrial control automation, smart home, automotive networking, communications, medical and other high-end industry PCBA and finished products high-end manufacturing services, the company provides domestic and foreign customers with circuit board production, circuit board patch processing to patch test one-stop solution.
What We Do
Specialized Expertise
- We provide professional and attentive electronic information products processing \OEM\ODM manufacturing services:
- We provide professional SMT chip processing | DIP processing \OEM\ODM services for products covering consumer electronics, commercial electronics, industrial control electronics, health care electronics, communication electronics and other fields.
- Depending on the customer’s needs, we can provide PCBA processing or finished products.
- We have rich experience in manufacturing products with high process difficulty, such as BGA, QFN, double-row QFN, and double-layer BGA component products, and can give professional support to our customers.
- We can work with customers for samples and small orders.

Global One-stop Electronic Manufacturing Service Provider
Fast Prototype and Volume Production
High Level Production Equipments
Advanced Technology Advanced Contract Manufacturing
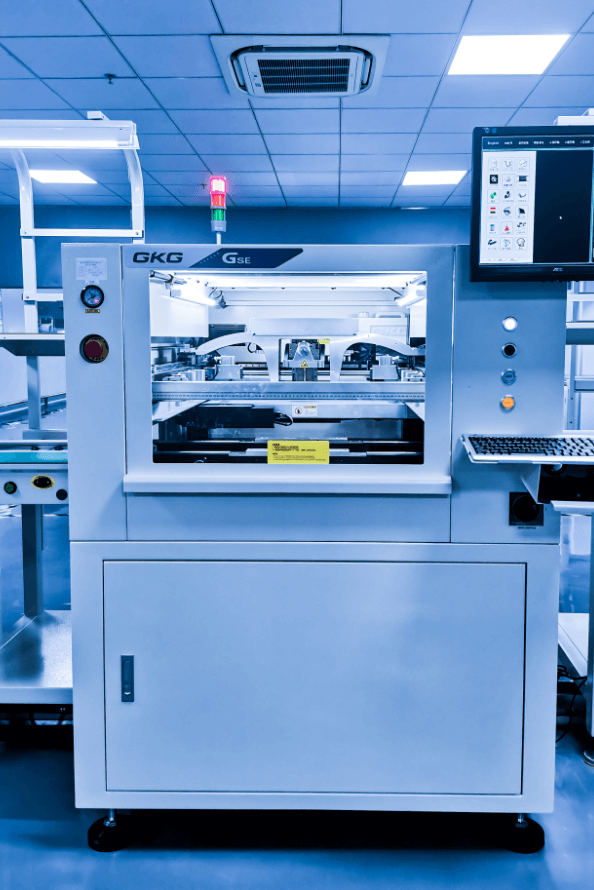

Solder paste printing machine
GKG automatic printing machine

X-Ray
2D 3D X-Ray
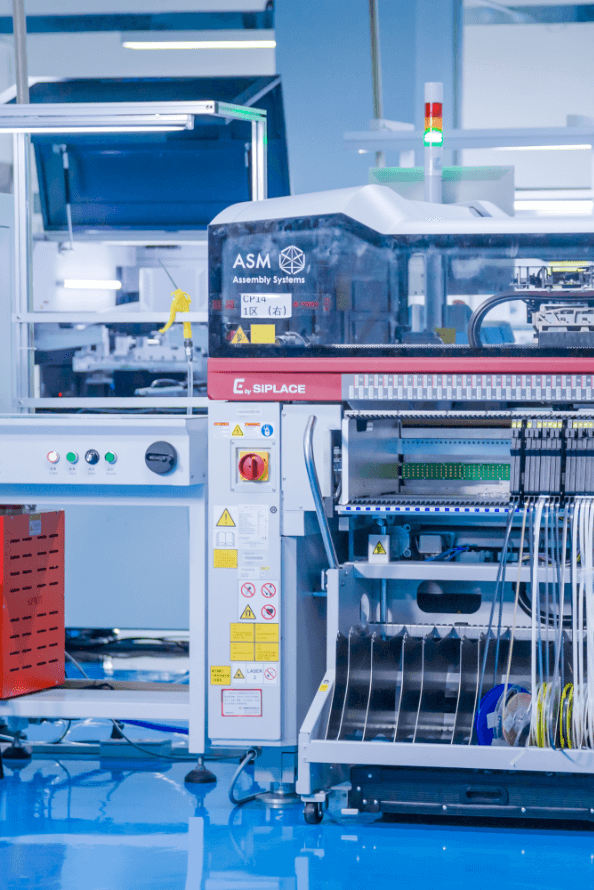
SMT Machine
Brand new Siemens E series placement machine
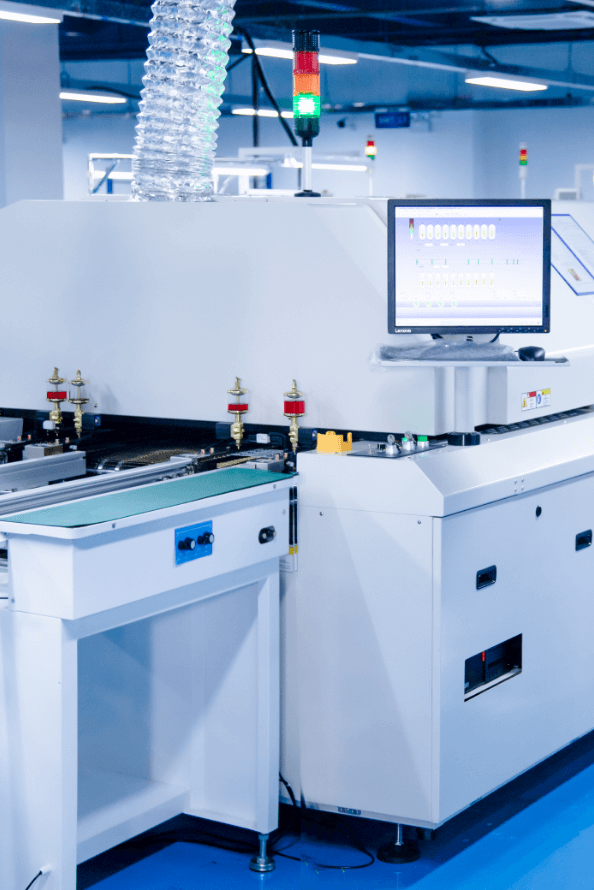

Reflow Soldering
10-12 temperature zone air reflow soldering and nitrogen reflow soldering
From Our Blog Posts
All about electronic manufacturing – PCB Manufacturing,SMT Assembly, PCBA Test
-
How to Make 3D Paper Snowflakes: Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
Making 3D paper snowflakes is a fun and easy craft activity that can be enjoyed by people of all ages. These beautiful snowflakes can be used to decorate your home during the winter season, and they also make great gifts for family and friends. To get started, all you need … Read more
-
Exit 3D Mode in Photoshop: Quick and Easy Steps
Exiting 3D mode in Photoshop can be a bit tricky, especially if you’re not familiar with the software. But don’t worry, it’s actually quite simple once you know what to do. In this article, we’ll show you how to exit 3D mode in Photoshop and get back to working in … Read more
-
How Much Does a 3D Ultrasound Cost? A Comprehensive Guide
A 3D ultrasound is a type of medical imaging that provides detailed, three-dimensional images of a developing fetus. Many expectant parents are interested in getting a 3D ultrasound to see their baby’s features and movements before birth. However, the cost of a 3D ultrasound can vary widely depending on a … Read more

Together We Will Drive Your Success
INDUSTRIES WE SERVE
High-end manufacturing service provider of industrial control industry, smart home, communication medical PCBA.

Security Industry
Security industry products include monitoring, burglar alarms, intrusion detectors, burglar alarm controllers, car alarm systems, electronic fences, etc.

Automotive Electronics
Window control panels, airbag systems, driving dynamics regulation (FDR or VDC), collision avoidance systems, seatbelt control, photo control
IOT Devices
Alcohol Detection for Bus Drivers, Agricultural Irrigation, Oil Pipeline Control, Blood Pressure Monitoring, Industrial Inspection, Gas Detection

Industrial control signals
With embedded industrial controllers and PLCs, robots, servo motors, sensors, industrial cameras, PLC programmable logic controllers

Medical Electronics
Sphygmomanometer, electronic thermometer, multifunctional therapeutic instrument, blood glucose meter, electric massage chair/bed, massage stick; massage whack; massage pillow, massage cushion, massage belt; qi and blood circulation machines; foot baths
Communications Electronics
5G Base Station, 4G Base Station, Logistics Handheld Devices, Face Recognition Devices,

Intelligent Home
Smart Door Lock, Smart Curtain, Smart Lighting, Smart Speaker, Mop-Sweep Robot, Smart Pet Feeder, Smart Pet Feeder, Smart Stir-Fryer, Smart Toilet

Military Electronics
Radar, microwave monolithic integrated circuits, laser rangefinders, night vision devices, as well as laser sights, communications, electronic countermeasures, TR components, phased array antennas

Smart Wearable
VR/AR, Smartwatch
Artist 3D, Make electronic innovation easier!
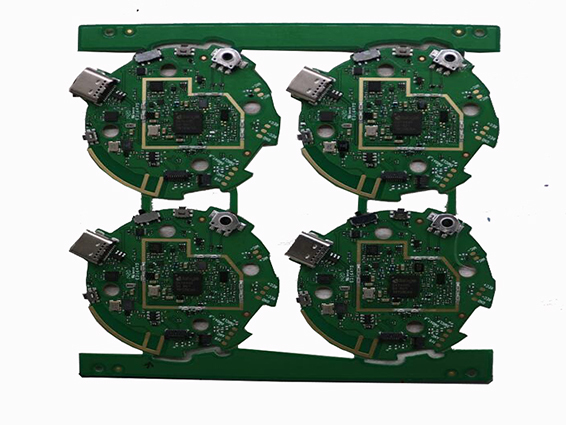

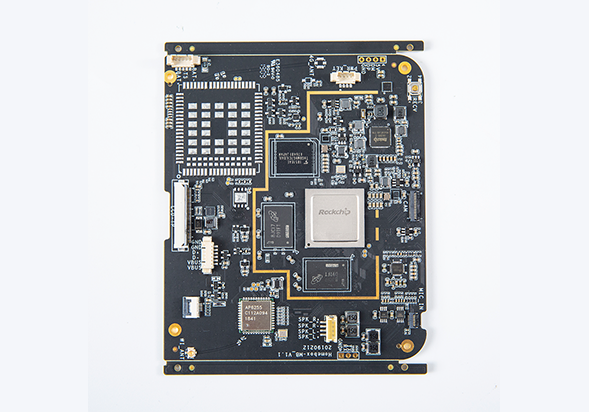
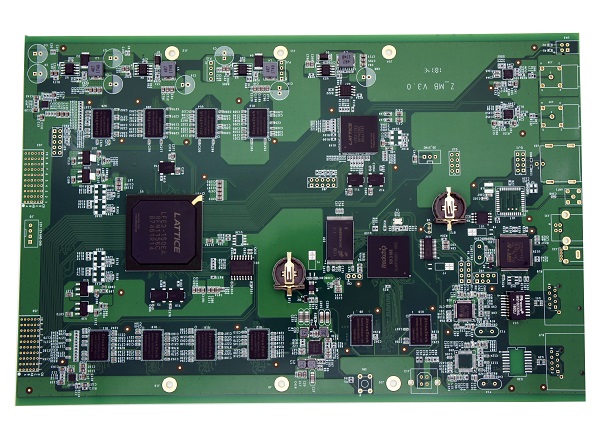
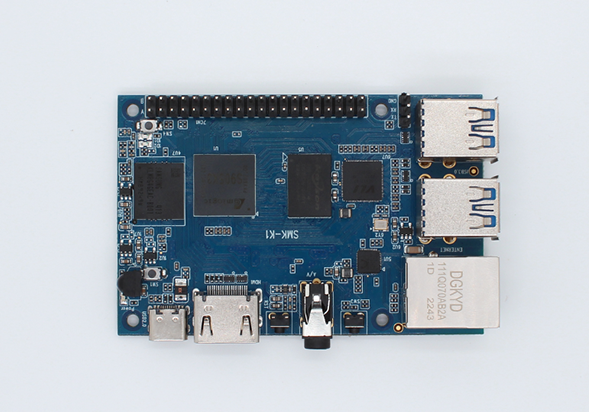
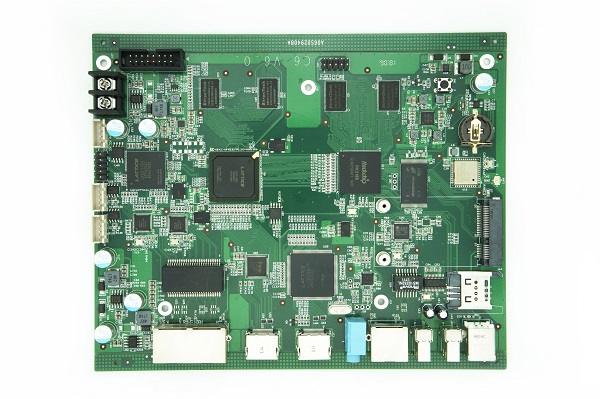
Watch Phone Board
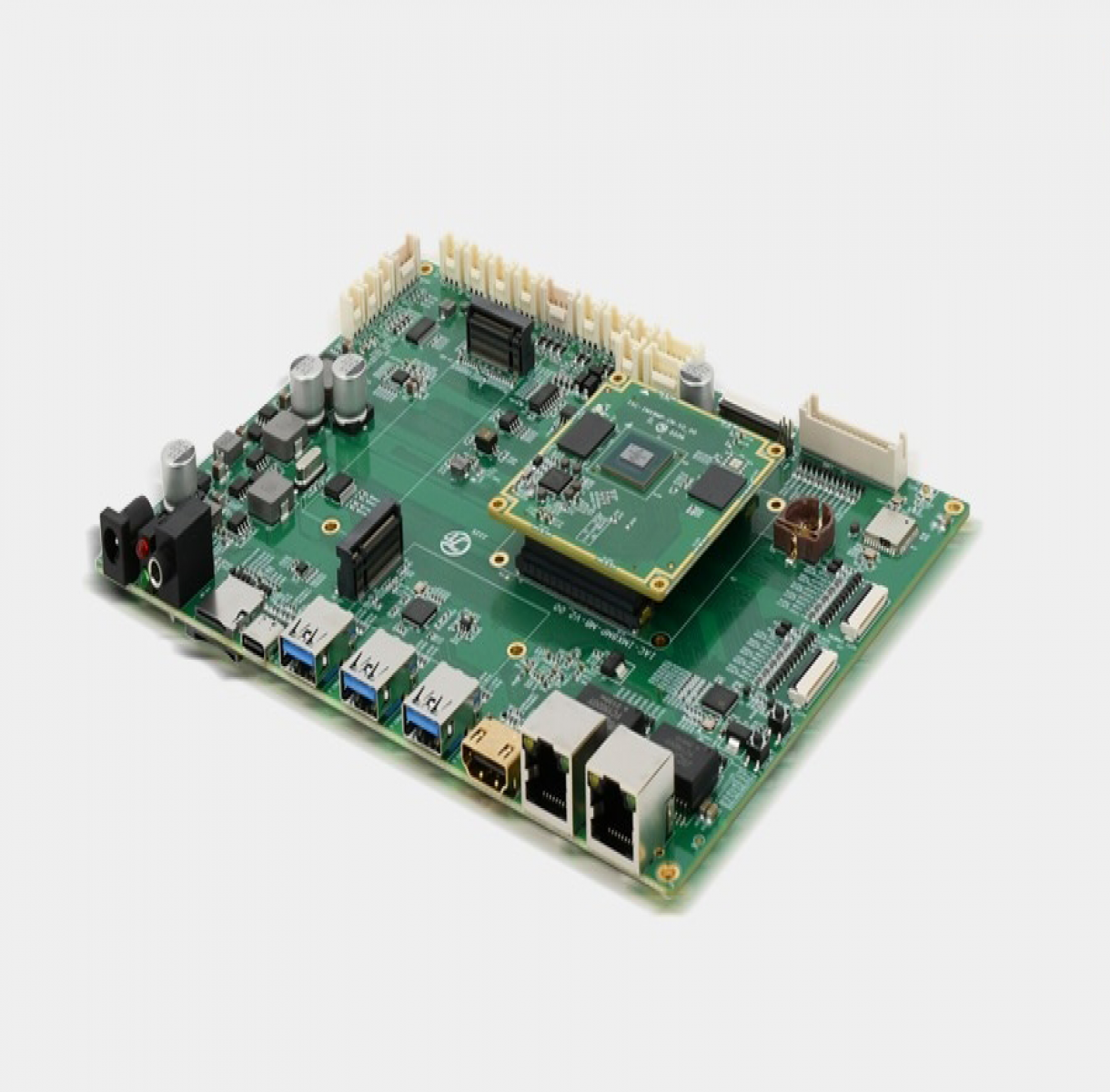

IAC-IMX8MP-Kit Development Board
3D Printer Main Board
Technical Capability
Global PCBA small and medium batch fast production service provider
SMT
SMD DIP
- Size:L50*w50~L510*w460mm
- Thickness:0.3mm~4.5mm
- Material:Rigid, Polymide,Rigid-flex
- Part Size:01005 ~ 45mm*98mm
- Part Pitch:IC 0.25mm,BGA-0.25mm
- Part Height:19mm
- SMT precision:chip±41μm,IC±37.5μm
- SMT capacity:1000万/D
PCB
Rigid RF HDI Board
- Layer:56
- PCB Thickness:7.0mm
- Min Thickness:0.33mm(4 Layer)
- Min width/spacing:3/3mil
- Copper Thickness:0.5 – 20oz
- Aspect ratio: 10:1
- Hole Tolerance: +/-0.05mm
- PTH Bore Tolerance: +/-0.05mm
- HDI steps: 4+N+4
Components
IC FPGA
- Original Agent Supply Chain
- Strategic Cooperation Big Data Platform
- Rapid delivery
- More than 30,000 commonly used components in stock
- Experienced supply chain team
- Full BOM component Sourcing
- Fast component system, 24H quotation support